Genetic Identification of Cell Types Underlying Brain Complex Traits Yields Novel Insights Into the Etiology of Parkinson's Disease
Genetic Identification of Cell Types Underlying Brain Complex Traits Yields Novel Insights Into the Etiology of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
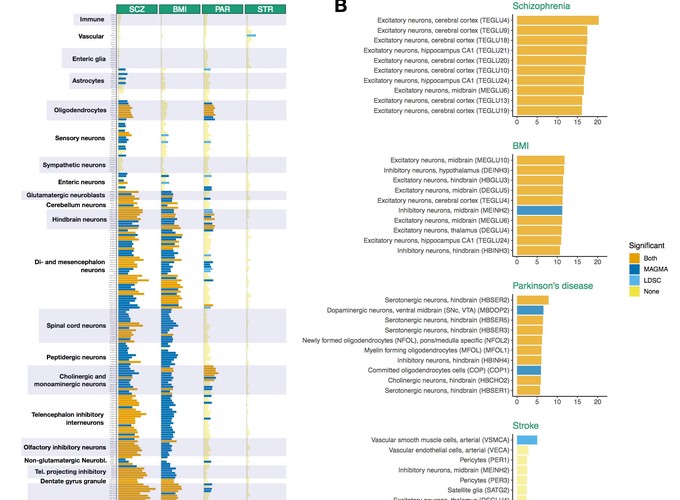
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have discovered hundreds of loci associated with complex brain disorders, and provide the best current insights into the etiology of these idiopathic traits. However, it remains unclear in which cell types these variants may be active, which is essential for understanding disease etiology and for disease modelling. Here we integrate GWAS results with single-cell transcriptomic data from the entire nervous system to systematically identify cell types underlying psychiatric disorders, neurological conditions, and other brain complex traits. We show that psychiatric disorders are predominantly associated with excitatory neurons from the cortex/hippocampus, medium spiny neurons from the striatum, diverse sets of midbrain neurons, and inhibitory neurons from the cortex/hippocampus. Cognitive traits were generally associated with similar cell types but their associations were driven by different genes. Neurological disorders were associated with different cell types, consistent with other lines of evidence. Notably, we found that Parkinsons disease is not only genetically associated with dopaminergic neurons but also with serotonergic neurons and cells from the oligodendrocyte lineage. Using post-mortem brain transcriptomic data, we confirmed alterations in these cells, even at the earliest stages of disease progression. Altogether, our study provides a solid framework for understanding the cellular basis of complex brain disorders and reveals a new unexpected role of oligodendrocytes in Parkinsons disease.
More detail can easily be written here using Markdown and math code.